iStent inject W
Also known as Trabecular Micro-Bypass
Medical Disclaimer: Information on this page is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
See our Terms and Telemedicine Consent for details.
Overview
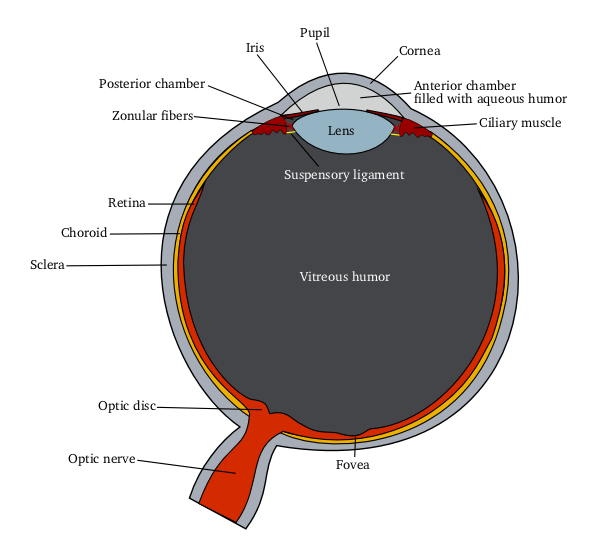
iStent inject W is a tiny implant used during cataract surgery to help lower eye pressure in adults with mild to moderate primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG). It belongs to a group of procedures called microinvasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS), which aim to reduce pressure with smaller incisions and faster recovery than traditional glaucoma surgeries. MIGS improves the flow of the eye’s natural fluid (aqueous humor) to protect the optic nerve over time.1
The iStent inject W system includes two heparin-coated titanium stents placed into the eye’s drainage system (trabecular meshwork and Schlemm’s canal) to create tiny bypasses for fluid outflow. It is FDA-cleared for use with cataract surgery to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) in adults with mild to moderate POAG.
People often choose iStent inject W when eye drops alone are not enough or are hard to use daily. The goal is to lower IOP and possibly reduce glaucoma medications after cataract surgery. The device’s W model features a wider proximal end for better visibility and placement.2
How the Procedure Works & Options
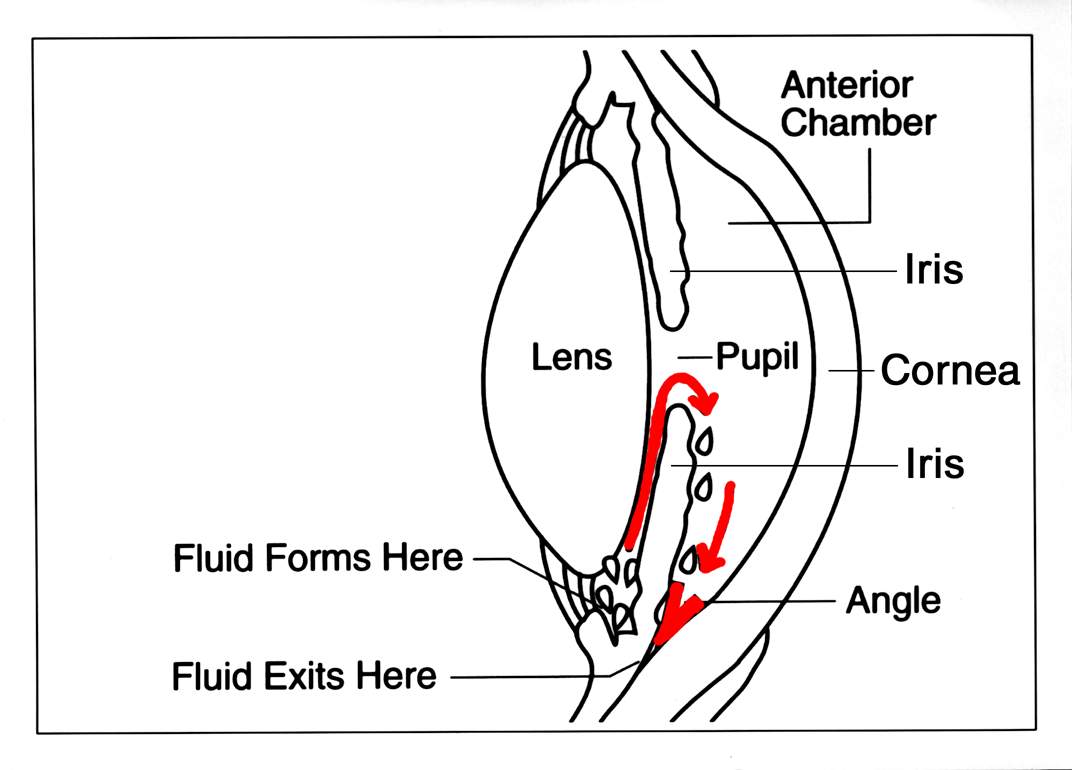
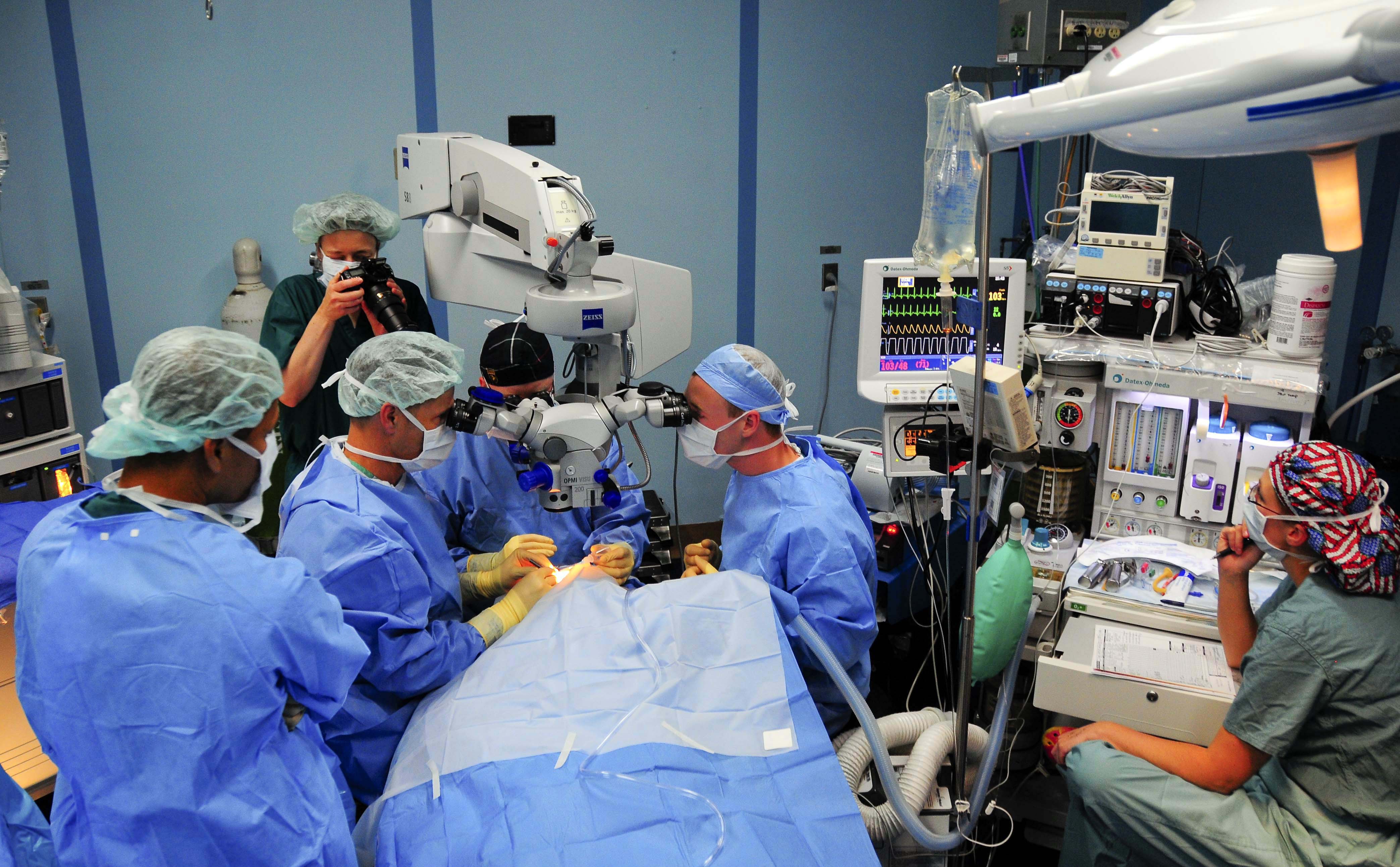
How it works: During cataract surgery, the clouded lens is removed and replaced with a clear lens implant. Right after, the surgeon uses a gonioprism lens to view the eye’s drainage angle. The iStent inject W injector delivers two tiny stents through the trabecular meshwork into Schlemm’s canal, creating micro-bypass channels to let fluid leave the eye more easily. This can lower pressure.3
The instructions describe placement steps and device size (~360 µm tall).
Options within MIGS:
- Some MIGS devices (like iStent inject W) target trabecular meshwork and Schlemm’s canal.
- Others act in the suprachoroidal space or under the conjunctiva.
Your ophthalmologist selects based on glaucoma type, anatomy, and goals.4 iStent inject W is only indicated with cataract surgery, not as a stand-alone procedure in the U.S.
Who Is a Candidate?
Good candidates: Adults with mild to moderate POAG already scheduled for cataract surgery. The angle must be open on gonioscopy so the surgeon can visualize and access the trabecular meshwork safely.5 Surgeons also consider medication burden and target IOP.6
Not candidates: People with angle-closure glaucoma, active eye inflammation, or secondary glaucomas listed in contraindications. Poor angle view (like corneal opacity) may make placement unsafe.
Is iStent inject W a Good Fit for Me?
Select your details to estimate suitability.
Cost and Price
Costs vary by insurance, surgeon, and setting. For Medicare patients, cataract surgery is generally covered under Part B as an outpatient service. Out-of-pocket costs depend on deductible, coinsurance, and plan specifics.7
MIGS device placement uses specific CPT codes; CMS guidance allows one unit per eye per day, even with multiple stents from the same insertion tool. Coverage depends on local policy and medical necessity.8
Tip: Ask your surgeon’s office for a cost estimate and check if prior authorization is required.
Benefits and Limitations
Benefits: May lower IOP after cataract surgery and reduce need for daily drops. A large randomized trial showed more patients reached pressure goals with fewer medications vs cataract surgery alone.9
Limitations & Risks: Only indicated with cataract surgery for mild/moderate POAG in the U.S. Risks include bleeding, inflammation, and need for more treatment later. Contraindications: angle-closure, some secondary glaucomas.10 Results vary; some still need drops or later procedures.
Recovery and Long-Term Care
Most patients follow standard cataract recovery: wear shield at night, avoid rubbing, use prescribed drops, attend follow-ups. AAO benchmarks recommend a check on day 1, then 1–2 weeks, with more visits over months.11
iStent inject W instructions emphasize angle visualization and postoperative pressure monitoring. If above goal, more therapy may be required.
You’ll get a device card noting the implant is MR Conditional; keep it with you and show other providers as needed.12
Latest Research & Innovations
Studies and meta-analyses report that trabecular MIGS with cataract surgery can lower IOP and reduce medications compared with cataract surgery alone, with favorable safety.13 Long-term data help set realistic expectations for IOP lowering, medication reduction, and safety signals.14
The W model features design updates (wider proximal end) for better visualization and stability.
Recent Peer-Reviewed Research
Phacoemulsification combined with trabecular meshwork-Schlemm canal-based minimally invasive glaucoma surgery in primary angle-closure glaucoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Fang Z, Song Y, Jin L, et al.
A case of two connected stents deployed during iStent inject W surgery.
Shimada A, Ichioka S, Ishida A, et al.
Roles of Toric intraocular Lens implantation on visual acuity and astigmatism in glaucomatous eyes treated with iStent and cataract surgery.
Ichioka S, Ishida A, Takayanagi Y, et al.
Next Steps
If you have mild to moderate POAG and a visually significant cataract, discuss iStent inject W with your surgeon. Bring your medication list, pressure history, and any issues using drops.15
Urgent signs: sudden eye pain, halos, headache, big vision change—seek urgent care.16
Kerbside can help you connect with a specialist for educational consults about MIGS; this is not a physician–patient relationship.
Trusted Specialists
Board-certified providers specializing in iStent inject W.


