XDEMVY
Also known as Lotilaner Ophthalmic Solution 0.25%
Medical Disclaimer: Information on this page is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
See our Terms and Telemedicine Consent for details.
Overview
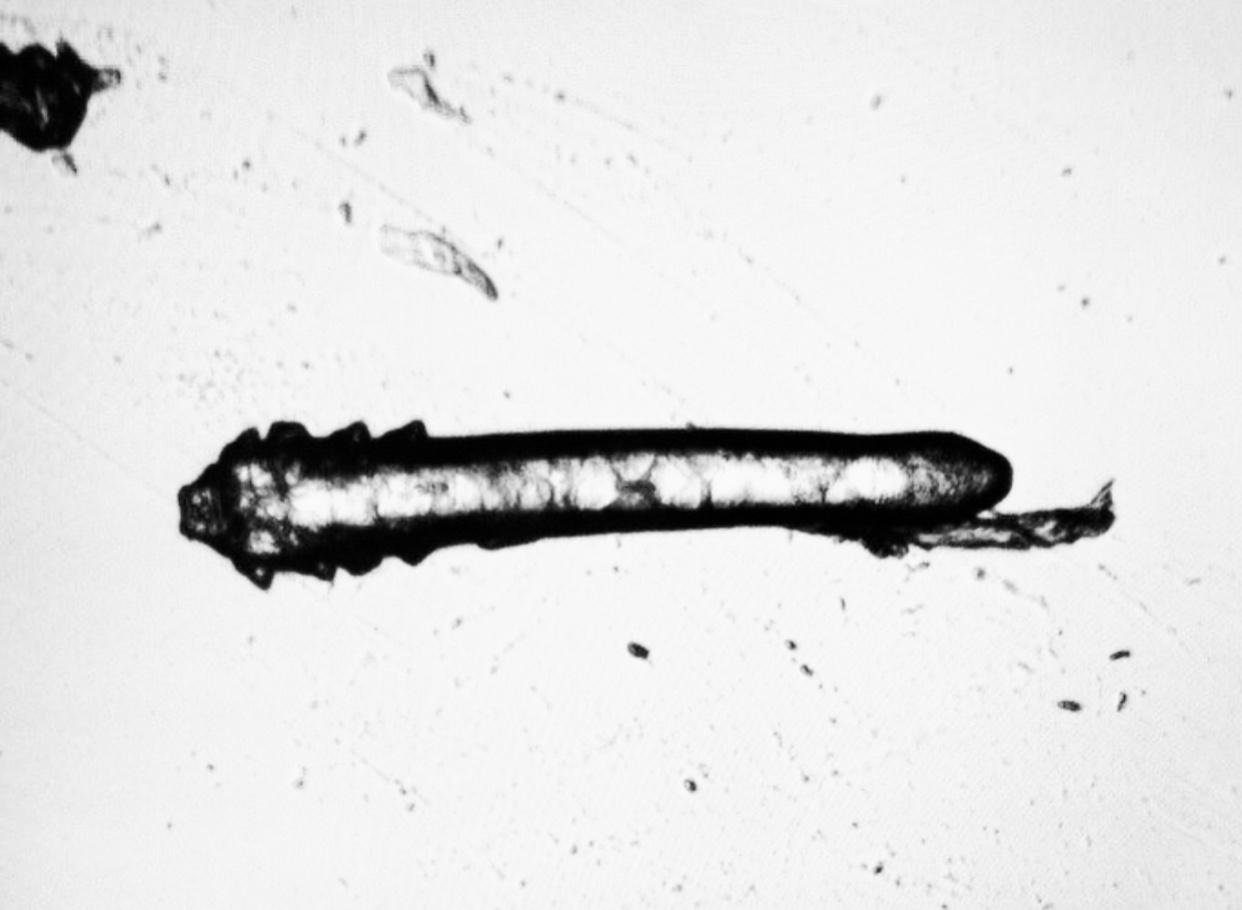
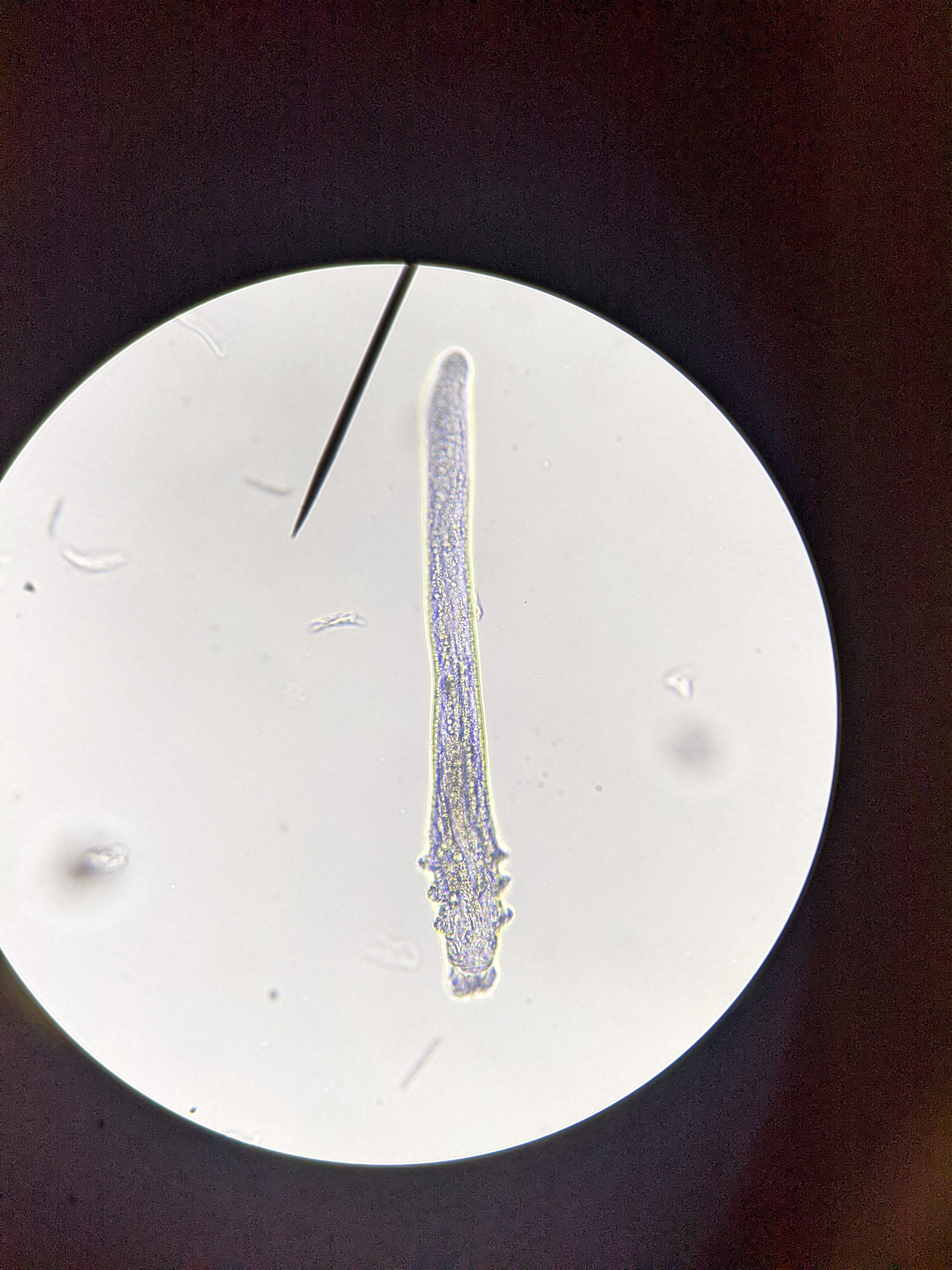
XDEMVY is a prescription eye drop that treats Demodex blepharitis—eyelid inflammation caused by an overgrowth of tiny mites that live around the eyelashes. The active ingredient, lotilaner 0.25%, is formulated as an ophthalmic solution and is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) specifically for this condition. 1 XDEMVY was approved based on two pivotal randomized clinical trials (SATURN-1 and SATURN-2) that enrolled more than 800 people with Demodex blepharitis, making it the first FDA-approved therapy targeting these mites. 2
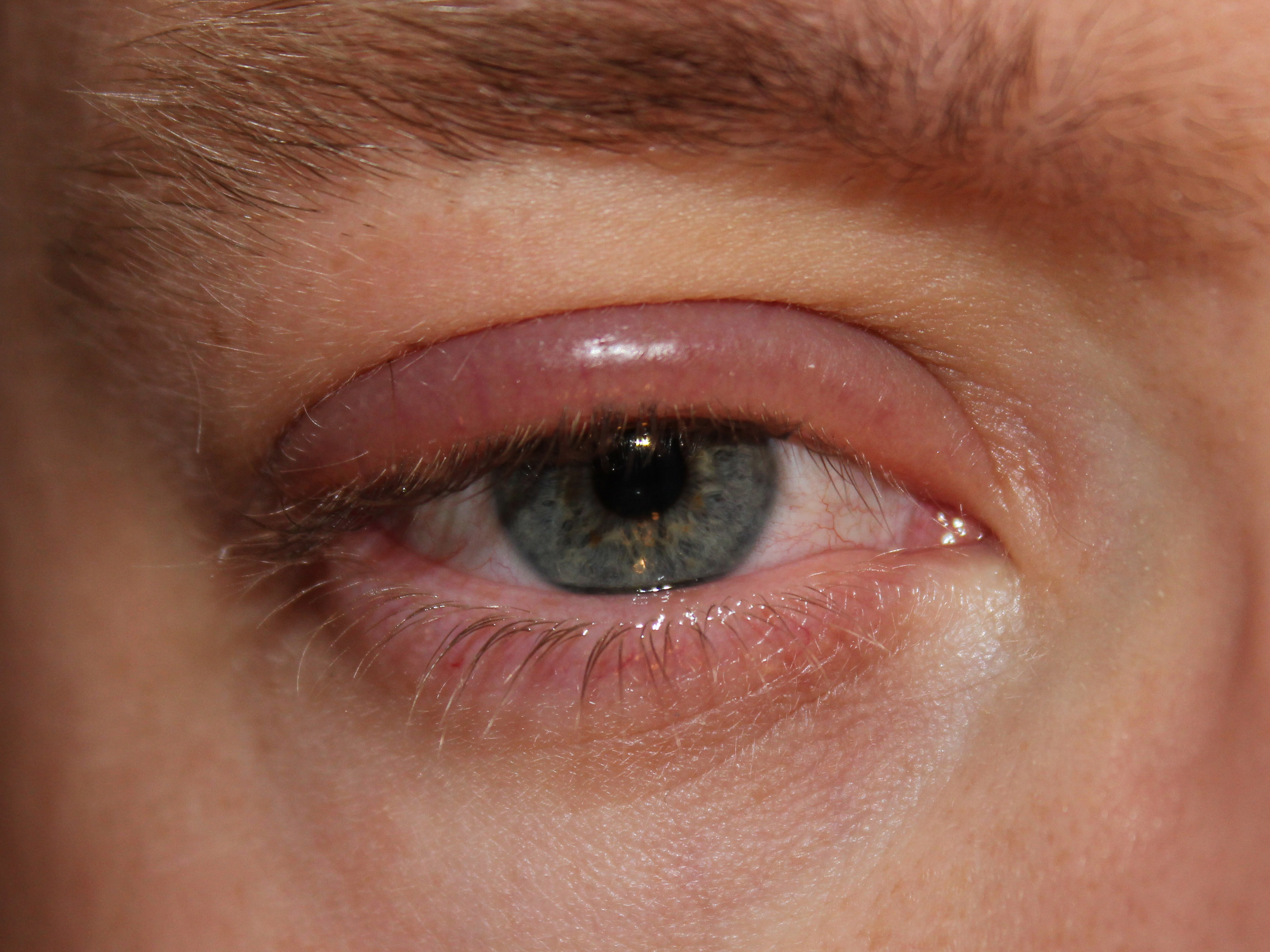
Why this matters: Demodex blepharitis can cause itching, redness, lash debris (called collarettes), and fluctuating vision. Treating the root cause—the mites—can reduce debris and irritation and help you get back to comfortable eyes.
How the Procedure Works & Options
How it works: Lotilaner belongs to the isoxazoline class. It selectively blocks mite-specific GABA-gated chloride channels, leading to paralysis and death of Demodex. The FDA clinical pharmacology review also confirms the approved dosing: one drop in each eye twice daily (about 12 hours apart) for 6 weeks. 3 Supportive laboratory research shows isoxazolines like lotilaner potently inhibit invertebrate GABA chloride channels while sparing mammalian receptors. 4
What to expect: Your clinician will show you how to instill drops without touching the bottle tip. Most patients complete a 6-week course.
Other options often discussed (sometimes combined with XDEMVY): warm compresses and lid hygiene; in select cases device-based care (e.g., IPL) for coexisting blepharitis or meibomian gland disease. Evidence for these supportive options exists for general blepharitis management but they do not eradicate Demodex mites. 5 Always follow your eye care professional’s plan.
Who Is a Candidate?
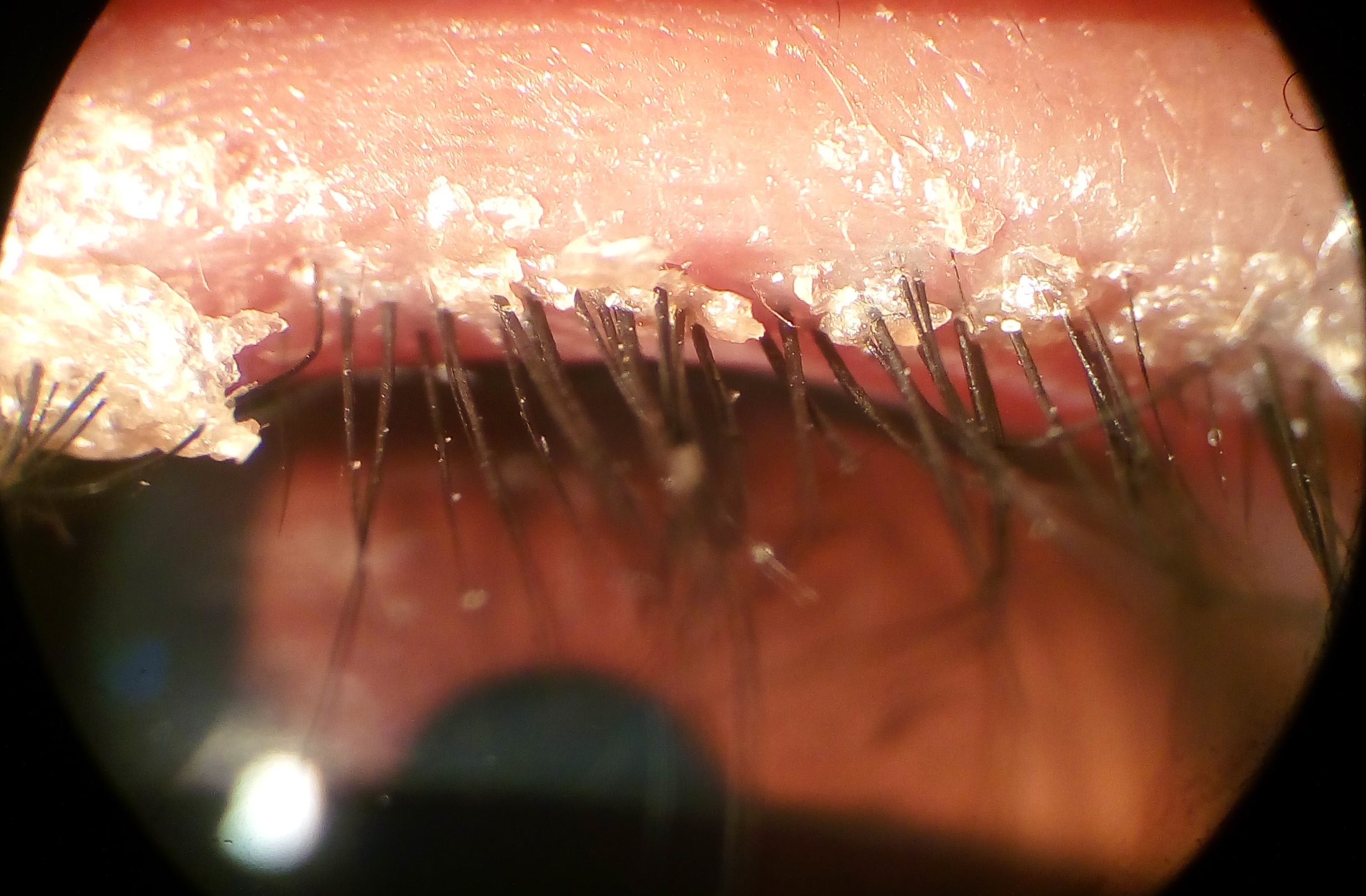
You may be a good candidate for XDEMVY if you have signs of Demodex blepharitis such as collarettes (cylindrical waxy debris at the lash base), lid redness, or itching, and your clinician confirms the diagnosis. Collarettes are a hallmark finding during a slit-lamp exam. 6 XDEMVY is FDA-approved for the treatment of Demodex blepharitis; your clinician will consider your overall eye health, medications, and history before prescribing. 1
Good to know: Contact lens users can usually still be treated (lenses are removed before dosing and reinserted after guidance from your clinician). Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, nursing, or have other eye conditions so they can tailor care appropriately.
Am I a Candidate for XDEMVY?
Select your details to estimate suitability.
Cost and Price
The out-of-pocket price of prescription eye drops can vary based on insurance, pharmacy, and location. Many patients use manufacturer savings programs or pharmacy benefit tools to lower costs. XDEMVY’s site lists access and savings resources and notes that coverage continues to expand across commercial and government plans. 7 You can also check plan coverage and typical copays using trusted pharmacy resources (for example, Medicare Part D plan details and copay ranges). 8
Tips to discuss with your clinic: prior authorization, patient assistance eligibility, and which pharmacy will dispense your drop so there are no delays. Your care team can help you navigate affordability options.
Benefits and Limitations
Benefits shown in trials: In SATURN-2, twice-daily lotilaner 0.25% for 6 weeks significantly improved collarette grade and eyelid redness versus vehicle, with many patients reaching clinically meaningful reduction in debris. 9 XDEMVY targets the root cause—Demodex—rather than only masking symptoms, which can help reduce recurrence of lash debris after a treatment course.
Limitations & side effects: The most common reactions in studies were instillation site stinging or burning; less common events included chalazion/hordeolum and punctate keratitis. Serious adverse reactions were rare. Always follow labeled dosing and precautions. 10
Response varies. Some patients may still need ongoing lid hygiene or other care for coexisting blepharitis or dry eye. Your clinician will personalize your plan.
Recovery and Long-Term Care
During treatment (6 weeks): Instill one drop in each eye twice daily, about 12 hours apart. Do not touch the dropper tip to the eye or lashes. Remove contact lenses prior to dosing and wait per your clinician’s guidance before reinsertion. If you miss a dose, use it as soon as you remember and then resume the usual schedule. 11
After the course: An observational extension of SATURN-1 followed patients months beyond therapy and reported sustained reductions in collarettes for many individuals, suggesting durable benefit after mite eradication in a subset. Your results may differ, and some people may eventually need retreatment based on symptoms and clinical signs. 12
Healthy eyelid habits—gentle lid hygiene, makeup removal, and addressing coexisting blepharitis—can support long-term comfort. Ask your clinician what ongoing steps fit your eyes.
Latest Research & Innovations
Since FDA approval, analyses continue to refine where XDEMVY fits in care. A pooled analysis of SATURN-1 and SATURN-2 (>800 patients) showed lotilaner significantly reduced collarettes and eyelid erythema and lowered mite density, with a safety profile consistent across studies. 13 A 2024 review in the American Journal of Ophthalmology summarizes clinical evidence and positions lotilaner as a targeted therapy for Demodex blepharitis, contrasting it with older off-label approaches (e.g., tea tree oil) that can be irritating. 14
What’s next? Ongoing work explores real-world durability, retreatment strategies, and integration with meibomian gland and dry-eye care—especially for patients with mixed blepharitis.
Recent Peer-Reviewed Research
Long-Term Outcomes of 6-Week Treatment of Lotilaner Ophthalmic Solution, 0.25%, for Demodex Blepharitis: A Noninterventional Extension Study.
Sadri E, Paauw JD, Ciolino JB, et al.
Efficacy and Safety of Lotilaner Ophthalmic Solution (0.25%) for the Treatment of Demodex Blepharitis: A GRADE Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational & Experimental Studies.
Talha M, Haris Ali M, Fatima E, et al.
Lotilaner Ophthalmic Solution 0.25% for Demodex Blepharitis: Randomized, Vehicle-Controlled, Multicenter, Phase 3 Trial (Saturn-2).
Gaddie IB, Donnenfeld ED, Karpecki P, et al.
Next Steps
If you see lash debris or have chronically irritated lids, the best first step is a comprehensive eye exam. Evidence from SATURN-2 supports the effectiveness of lotilaner for Demodex blepharitis, and academy summaries highlight its clinical significance. 15 FDA resources also describe who was studied and overall benefits and risks to help you and your clinician decide. 16
The most relevant specialist: a cornea/external disease ophthalmologist (or an optometrist experienced in ocular surface disease). You can connect with the right specialist on Kerbside for a medical education consult—this is not a physician–patient relationship and isn’t emergency care, but it can help you prepare informed questions for your next visit.
Trusted Specialists
Board-certified providers specializing in XDEMVY.
